
Trumpet: device of the instrument, history, sound, types, playing technique, use
Contents
Most members of the brass group are of non-musical origin. People needed them to give signals during the hunt, to approach danger, to collect military campaigns. The pipe is no exception. But since the beginning of the XNUMXth century, it has become part of the orchestra, sounds in symphonic, jazz music, as well as solo.
Pipe device
The principle of the sound of wind musical instruments lies in the vibrations and fluctuations of the air column inside the tube. The longer it is, the more opportunities it gives the musician. At the pipe, it has a length of up to 150 centimeters, but for reasons of compactness it bends twice, reducing the length of the instrument to 50 cm.

The tube has the shape of a cylinder with a diameter of just over a centimeter, it gradually expands, turning into a socket. Manufacturing technology is complex. It is important to correctly calculate the degree of expansion of the socket so that it corresponds to the length of the main channel.
Interestingly, there is the longest pipe in the world with a length of 32 meters and a socket diameter of more than 5 meters. It is clear that a person will not be able to play on it. Air is supplied to the channel by means of a compressor.
The instrument consists of three parts: a mouthpiece, a pipe and a bell. But this is a primitive and far from complete idea of the instrument. In fact, there are more important components in it. Among the details:
- mouthpiece – connects the ear pads to the main channel;
- the first, second, third and tuning crowns – with the help of the crown of the general system and its extension, the instrument is tuned, the rest are used for maintenance;
- valves – a system of valves, when closed, a change in the sound effect occurs;
- drain valve – a technical device that is not involved in sound extraction.
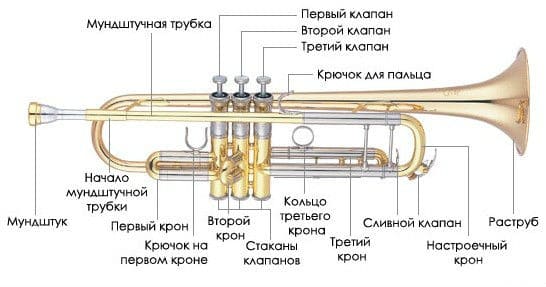
The tubes and components of the instrument are made mainly of copper and copper alloys, the luster of the body is given by lacquer, nickel or silver plating.
History of the tool
Wind instruments appeared long before the invention of melodic ones. It is known that people learned to trumpet three centuries before our era. In ancient Egypt, there was a special technology by which pipes could be made from a single sheet of metal.
During excavations in Egypt, pipes made of wood and shells were found. And in the tomb of Tutankhamun, tools made of silver and bronze were found.
In the Middle Ages, all troops were equipped with trumpeters, their main task was to transmit command orders to army units. In between wars, the instrument was used to attract the attention of spectators at jousting tournaments and on holidays. Its sound notified the residents of cities about the arrival of important people or the need to gather in the square to announce decrees.
In the Baroque era, the heyday of European academic music begins. The sound of the trumpet is included in orchestras for the first time. Despite the fact that the instrument made it possible to extract only the diatonic scale, musicians appeared who masterfully mastered the technique by changing the position of the lips.

But at the end of the XNUMXth century, stringed and melodic instruments flourished, and the trumpet, limited in its performance capabilities, faded into the background in the orchestra. It again begins to sound actively only closer to the middle of the XNUMXth century. By this time, the craftsmen had improved the design by introducing a valve system of three valves into it. They expanded the capabilities of the instrument, allowing it to change the scale, lowering the sound by a tone, a semitone and a tone and a half. The trumpet gained the ability to extract a chromatic scale, and after a number of device improvements, the problem of fluency and change in timbre was solved.
The history of the wind brass musical instrument knows many outstanding trumpeters. Among them is Maurice André, recognized as “the trumpeter of the 200th century.” He treated the trumpet as one of the main concert instruments, taught at the Paris Conservatory, and recorded more than XNUMX discs. Other famous trumpeters include Louis Armstrong, Freddie Hubbard, Sergey Nakaryakov, Arturo Sandoval.
System, range, registers
The main one in the orchestra is the trumpet in the system “B-flat” – “Do”. Notes are written in the treble clef a tone higher than the real sound. In the lower register, the instrument produces a gloomy sound, in the middle – soft (piano), militant, persistent (forte). In a high register, the trumpet calls the listener with a sonorous, bright sound.
In the middle register, the trumpet shows remarkable passage possibilities, thanks to its technical mobility it allows you to compose arpeggios.
In Europe and America, the “analogue” of this instrument in the “Do” system has found the greatest distribution. Western musicians find many advantages of its use, ease of sound production in the upper register and the ability to realize the range from “Mi” of a small octave to “C” of the third.

Pipe varieties
Other types of pipes are less commonly used:
- alto – a variety is used to produce sounds of a low register, the “Sol” system, often in a symphony orchestra this type replaces the flugelhorn;
- piccolo – an improved model with an additional valve, tuned to “Sol” or “La”, has a small mouthpiece;
- bass – is tuned in “C”, but is able to sound an octave lower than that of a conventional pipe.
In modern symphony orchestras, the bass trumpet is almost never used; it is replaced by the trombone.

Play technique
The performer holds the instrument with his left hand, with his right he acts on the valve system. To learn how to play, you need to understand that the extraction of harmonics occurs due to the embouchure, that is, changes in the position of the lips, tongue, and facial muscles. Lips during sound extraction acquire a certain rigidity, become tense. In the process, the musician lowers the sound with valves.
Due to the fact that the consumption of breath during the performance of music on the trumpet is small, the instrument allows you to perform various techniques, passages, arpeggios. Brilliant staccato variations are realized in the middle register.
Professionals actively use special devices called mutes and are inserted into the bell. Depending on the shape of the mute, the trumpet will sound quieter or louder. So in jazz, “fungus” is most often used, which makes the sound soft, velvety.

Pipe use
A large orchestral instrument is used in music to give it a dramatic character, to create tension. The sound is quite expressive, even if it sounds quiet. Therefore, the trumpet in the compositions represents heroic images.
Nowadays, trumpeters can perform solo, or they can make up entire orchestras. In 2006, an ensemble of 1166 trumpeters performed in Oruro, Bolivia. He is included in musical history as the most numerous.
The instrument is used in various musical genres. He is a permanent member of the jazz, symphony and brass band, his sounds are sure to accompany military parades.

Notable trumpeters
The most famous were musicians with brilliant technique. Among the virtuosos who dedicated their lives to promoting the instrument is Arturo Sandaval, who studied it from the age of 12 and received 10 Grammy awards during his lifetime.
American trumpeter Clark Terry has left his mark on jazz culture. He performed all over the world, gave free lessons, had a unique technique and virtuosity.
In 1955, the trumpet of another jazz legend, Dizzy Gillepsy, was sold at Christie’s auction. The famous instrument was branded as “Martin Committee” and sold for $55.
Everyone knows the story of a guy from a poor New York family, Louis Armstrong. His fate was difficult, as a teenager he committed crimes, stole and could spend his whole life behind bars. But one day at the correctional facility he heard a trumpet and became interested in studying the instrument. His first concerts were street performances, but very soon Armstrong became one of the most famous performers, distinguished by his radiant technique. Louis Armstrong gave the world a unique musical legacy of jazz.





