
Recorder: what is it, instrument composition, types, sound, history, application
The sound of the flute is gentle, velvety, magical. In the musical culture of different countries, it was given serious importance. The recorder was the favorite of the kings, its sound was heard by the common people. The musical instrument was used by wandering musicians, street performers.
What is a recorder
The recorder is a whistle-type wind instrument. A pipe is made of wood. For professional instruments, valuable species of mahogany, pear, plum are used. Inexpensive recorders are made of maple.

One of the museums in the UK holds the largest fully functional recorder made from specially treated pine. Its length is 5 meters, the diameter of the sound holes is 8,5 centimeters.
Plastic tools are also common. They are stronger than wooden ones and have good musical capabilities. Sound extraction is carried out by vibrating a column of air, which is blown through a hole at the end. The longitudinal flute resembles a whistle in terms of sound extraction. It is used in the early stages of learning. The family combines different types of instruments related to the playing technique: whistle, pipe, pipe.
Recorder device
In its structure, the instrument resembles a pipe. The sound range is from “to” II octave to “re” IV. It differs from the flute in the number of holes on the body. There are only 7 of them. There is one more on the back side. It’s called an octave valve.
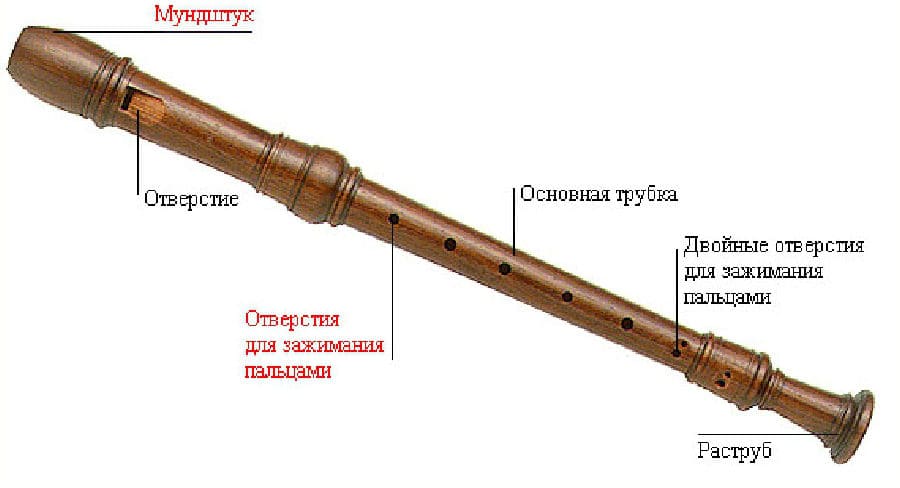
Another difference between a recorder and a flute lies in the structure. The name of the instrument was due to the wooden cork built into the whistle device – the block. It closes free access to the air stream, passing it through a narrow channel. Passing through the gap, the air enters the hole with a sharp end. In this block, the air stream is dissected, creating sound vibrations. If you clamp all the holes at the same time, you get the lowest sound.
The soprano recorder is a full-sounding representative of the brass family with a full-fledged chromatic scale. It is standardly tuned in the notes “do” and “fa”, recorded in the scores in real sound.
History
Information about the recorder is reflected in the documents of the medieval period. The instrument was used by itinerant musicians. For a soft velvety sound in Italy, he was called a “gentle pipe”. In the XNUMXth century, the first sheet music for the recorder appeared. Having undergone a number of design changes, it began to sound better. The appearance of a hole on the back side expanded the timbre, made it more velvety, rich, and light.
The heyday of the recorder came in the middle of the XNUMXth century. Then the most famous composers used the instrument to give the works a special flavor. But after a few decades, it was supplanted by a transverse flute, which has a large range of sound.
The renaissance era for the “gentle pipe” began when the creation of ensembles performing authentic music began. Today it is used to perform rock and pop music, ethnic works.

Types of recorders and their sound
There is a German (German) and an English (Baroque) system for the structure of a longitudinal pipe. The difference between them is the size of the fourth and fifth holes. The German system recorder is easier to master. By clamping all the holes and opening them in turn, you can play the scale. The disadvantage of the German system is the difficulty in extracting some semitones.
The pipe of the baroque system sounds cleaner. But even for the execution of the basic tones, complex fingering is required. Such tools are used by professionals, beginners are advised to start with the German system.
Differences also exist in the type of tonality. Pipes come in various lengths – up to 250 mm. The variety determines the tone. In terms of pitch, common varieties are:
- soprano;
- soprano;
- alto;
- tenor;
- too.

Different types can sound within the same ensemble. The simultaneous participation of pipes of different systems allows you to perform complex music.
The alto longitudinal pipe sounds an octave below the sopranino. The soprano is tuned in C to the first octave and is considered the most common kind of “gentle flute”.
Less common are other varieties:
- subcontrabass in the “fa” system of the counteroctave;
- great bass or grossbass – tuned to “to” a small octave;
- harkline – the highest range in the F scale;
- sub-contrabass – the lowest sound in the “fa” of the contra-octave;
- subgrossbass – in the system C of a large octave.
The XNUMXth century in musical culture was marked by the return of the recorder. The instrument was actively used by famous performers: Frans Bruggen, Markus Bartolome, Michala Petri. He gives special colors to the compositions of Jimi Hendrix, the Beatles, the Rolling Stones. The longitudinal pipe has many fans. In music schools, children are instilled with special respect for the instrument on which the kings played music, they are taught to play different types of recorder.





