Accordion trivia. Various varieties of chorden.
 Not only the accordion
Not only the accordion
It is sometimes difficult for the average observer, not related to music, to grasp the various types of accordion and instruments of a similar structure belonging to this musical family. Most of the society uses a very simplified division into button and keyboard accordions, calling them most often harmonies. And yet we have a whole range of accordion instruments, such as: bayan, bandoneon or concertina. Despite their visual similarity and sound, they are completely different instruments in terms of systems and playing technique. Similarly to the guitar, violin and cello, each of these instruments has strings, but each one plays differently and uses different techniques.
What are the differences between the various instruments?
Accordion it is an instrument with which chords can be extracted and this is one of the main characteristics that distinguishes it from a bandoneon or concertina. There are at least a dozen bass generating systems, but the most common standard is a stradella bass manual. Although here we can also find some variations, e.g. in the row of basic basses, it does not necessarily have to be in the second row, only e.g. in the third one. With this arrangement, the second row will have major thirds basses, i.e. within a major third from the base row, and the first row will have minor thirds, the so-called at a distance of a minor third from the order of the basic bass. Of course, the stradell standard, the most common one has a bass arrangement, where in the second row we have basic basses and in the first row we have third octave basses. The remaining rows are typical chords: in the third row major, fourth minor, fifth seventh and diminished in the sixth row. We can also find accordions with additional rows, the so-called baritone or with a converter, i.e. a switch that changes the chord bass to a melodic manual. As you can see in the case of the accordion, we have a dozen or so solutions, and when it comes to the bass side, the registers can properly set the configuration of a given chord. As for the right hand, there are also different systems here, and apart from the basic standard division into a keyboard and a button system, the latter also has its own variations. In Poland, the most common is the button standard from the so-called with a B bar, but you can meet a button with the so-called with a C-neck, which is very popular in Scandinavia.
bandoneon instead, it is a variation of a button harmony with the most common 88 or more buttons. It has a rectangular structure and is often confused with a concertina. It is quite a difficult instrument to learn as each button produces a different sound to stretch and another to close the bellows. This makes mastering and assimilating the scheme of this instrument not the easiest task. Without a doubt, Astor Piazzolla was the most recognizable bandoneonist.
Concertina characterized by a hexagonal structure and was the prototype of the bandoneon. There are two basic versions of this instrument: English and German. The English system is single-voice on both sides and weaves the notes of the scale between the two hands, allowing for quick melodies. The German system, on the other hand, is bisonoric, thanks to which it significantly expands the number of votes.
They go down however, it is a variation of the accordion of Russian origin with a three-, four- or five-row arrangement of buttons on the melodic side. In terms of visuals and playing technique, it does not differ much from the standard button accordion with a converter, but we can find other design solutions in it. These top-shelf Bajans are characterized by beautiful deep organ sounds.
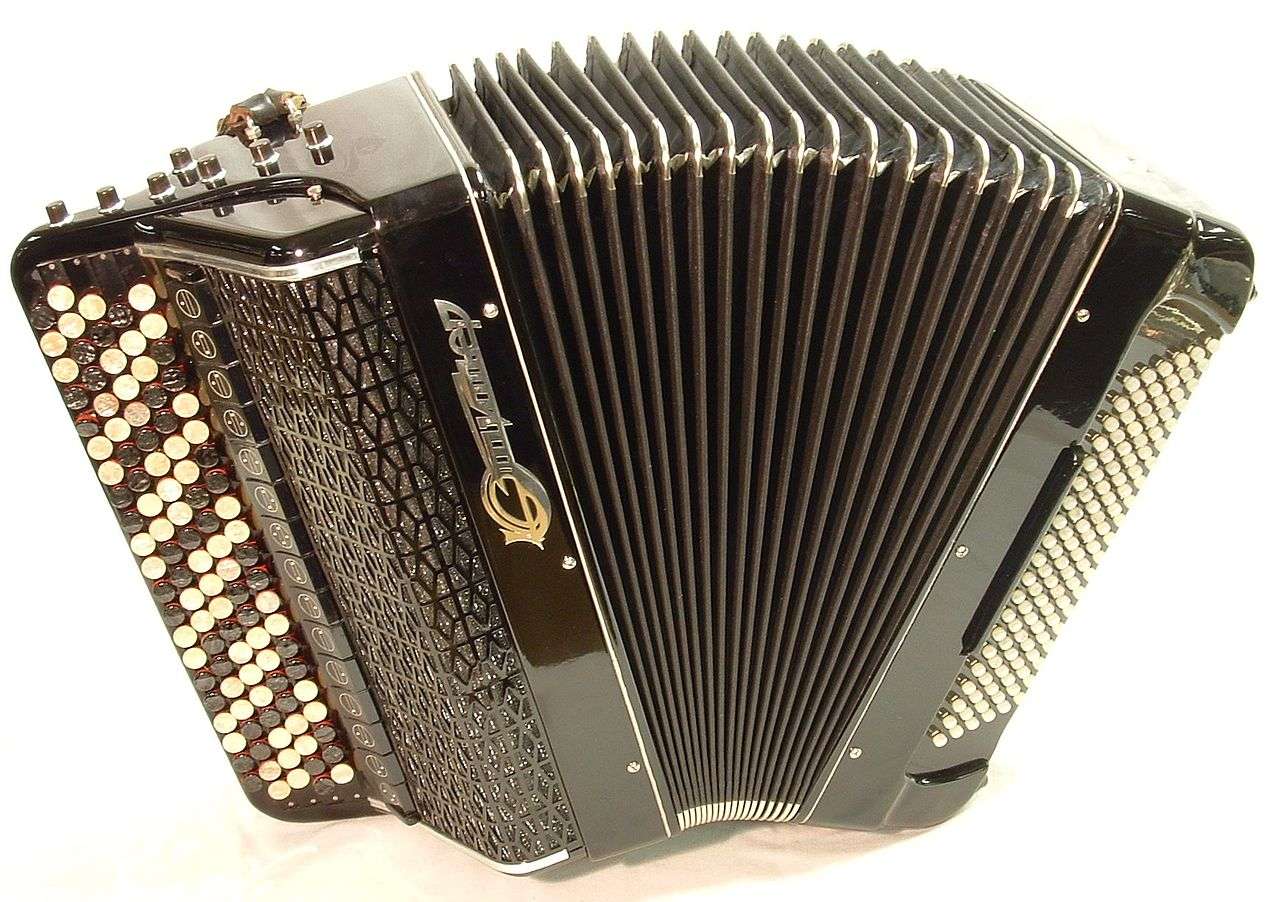

Harmony
All the instruments described above can be colloquially called harmony, although in fact this name is reserved in the music world for a specific group of instruments from this family. Among other things, in folk music the so-called harmonies, which also had their variations depending on the region of origin. In the Polish countryside you could meet the so-called Polish harmonies, the structure of which was modeled on the combination of structural elements of harmony and harmonies. They had a manual and a foot bellows. Thanks to the use of foot bellows, the manual bellows was almost completely relieved and was only used to emphasize individual notes. On the melodic side, there could be buttons or keys, and also in different variations, e.g. two or three rows. If we looked at individual regions of Poland and Europe, in every corner we can find some interesting, innovative technical solutions characterizing various types of harmony.
Summation
The family of wind instruments based on straight-through reeds as to blow is very large. Visually, of course, we will notice some differences between individual instruments, but without a doubt the biggest difference is in the playing technique itself. Each of these instruments has a different structure, and thus each plays differently. However, undoubtedly, the common feature is that all these instruments can sound great and bring a lot of joy to both the audience and the performer.