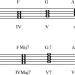About triads
Contents
Playing a musical instrument involves the use of chords . Among them, triads are popular.
Let’s analyze this concept, the main varieties and why it is important to determine triads by ear.
Chord
This is a rhythmically simultaneous combination of several sounds of different pitch. Classical harmony considers the chord to be sounds that are arranged in thirds. For the first time such a designation was expressed by J. Walter in 1732. The ear perceives the combination of musical sounds as a whole. They are located at distances from each other, which are called intervals. The sounds of the a chord are built from bottom to top – these are prima, third and fifth.
To create a chord , you need to pick up at least 3 sounds.
Triad
This is the name of the chord , consisting of 3 sounds, which are placed in thirds. In addition to the seventh chord and nonchord, the triad is one of the main chords used in music. To designate it, two numbers are used – 5 and 3.
Types of triads
 There are 4 types of triad:
There are 4 types of triad:
- Major – consisting of a major and a minor third. Here the consonant interval is a pure fifth: it is located between the extreme sounds.
- Minor – including minor and major thirds. In another way, it is called “small”. The consonant interval here is also a pure fifth.
- Augmented – contains 2 major thirds. Between the extreme sounds, the dissonant interval is an enlarged fifth.
- Diminished – consists of 2 minor thirds and a diminished fifth as a dissonant interval.
More clearly:

How to learn to distinguish by ear
In music schools, students are offered exercises in solfeggio lessons to analyze chords by ear. They teach to recognize sounds in comparison and remember how they sound. To make it easier to remember, triads can be characterized as follows:
- The major has a bright, confident and light sound.
- In the minor key, it is also confident, but with a hint of depression, sadness, darkness.
- Augmented triad has a bright but unstable sound. He immediately draws attention to himself.
- A diminished triad has an unstable sound, but compared to an enlarged triad, it is perceived concisely and faded.
Appeals
When prima, third and fifth are arranged from bottom to top, this is the main arrangement of sounds in a triad.
When the order of sounds changes, when the fifth or third acts as the lower one, there is an inversion, that is, a rearrangement of sounds.
There are two types of inversions for triads:
- A sixth chord is a variation where the octave is shifted up. It is marked with a six.
- Quartz-sextakkord – an appeal involving the transfer of a third and a prima an octave higher. It is designated 6/4.
Let’s look at examples
Do-Mi-Sol is an example of a major triad. When inverted, you can move the note C up an octave without touching the rest of the sounds. So it turns out Mi-Sol-Do – a sixth chord. To perform an inversion in it, it is enough to move Mi up a pure octave. It turns out a quarter-sextakkord, consisting of the notes Sol-Do-Mi. When performing one more inversion, there is a return to the original major triad.
Answers on questions
| What is a chord ? | A combination of at least 3 sounds of different pitches. |
| What is triad? | A 3- note chord consisting of thirds. |
| Is it possible to identify triads on your own? | Yes. |
| How to identify triads by ear? | Compared. Major sounds seem cheerful, minor sounds sad, etc. |
Useful, in our opinion, video
Conclusion
In musical practice, the most used type of chord is a triad. There are 4 varieties of it: major, minor , increased and decreased. The musician needs to develop the skill of identifying triads and chords in general by ear, which is useful when performing or creating compositions. Triads have two appeals – a sixth chord and a fifth-sixth chord.