
Trombone: what is it, instrument composition, sound, history, types
Contents
During the archaeological excavations of Pompeii, buried under the volcanic ash of Vesuvius in 79 BC, historians discovered bronze trumpets with gold mouthpieces carefully packed in cases. It is believed that this musical instrument is the predecessor of the trombone. “Trombone” is translated from Italian as “big pipe”, and the shape of the ancient find resembled a modern brass musical instrument.
What is a trombone
No symphony orchestra can do without a powerful sound, which is used to convey tragic moments, deep emotions, gloomy touches. This function is usually performed by a trombone. It belongs to the group of copper embouchure bass-tenor registers. The tool tube is long, curved, expanding in the socket. The family is represented by several varieties. The tenor trombone is actively used in modern music. Alto and bass are used very rarely.

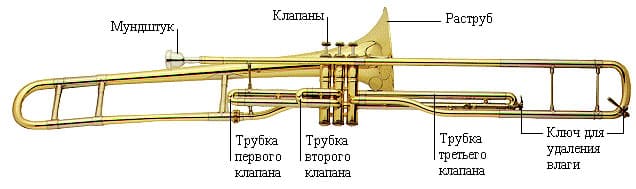
Tool device
The main difference from other representatives of the copper wind group is the equipment of the case with a backstage. This is a curved tube that allows you to change the volume of air. Thus, the musician can extract the sounds of the chromatic scale. The special structure makes the instrument more technical, opens up opportunities for a smooth transition from note to note, the performance of chromatises and glissando. On the trumpet, horn, tuba, the wings are replaced by valves.
Sound is produced by forcing air through a cup-shaped mouthpiece that is inserted into the trumpet. The backstage scale can be of the same or different sizes. If the diameter of both tubes is the same, then the trombone is called single-pipe. With a different scale diameter, the model will be called a two-gauge.
What does a trombone sound like?
The instrument sounds powerful, bright, inviting. The range is within the “G” counter-octave to “F” of the second octave. In the presence of a counter-valve, the gap between the “b-flat” of the counteroctave and the “mi” of the large octave is filled. The absence of an additional element excludes the sound production of this row, called the “dead zone”.
In the middle and upper registers, the trombone sounds bright, saturated, in the lower – gloomy, disturbing, ominous. The instrument has the unique ability to glide from one sound to another. Other representatives of the copper wind group do not have such a feature. The slide of the sound is provided by the rocker. The technique is called “glissando”.
To muffle the sound, a mute is often used. This is a pear-shaped nozzle that allows you to change the timbre sound, muffle the sound intensity, add variety with unique sound effects.
History of the trombone
In the middle of the XNUMXth century, rocker pipes appeared in European church choirs. Their sound was similar to the human voice, due to the movable tube, the performer could extract a chromatic scale, imitating the timbre features of church chanting. Such instruments began to be called sakbuts, which means “to push ahead of you.”
Having survived small improvements, sakbuts began to be used in orchestras. Until the end of the XNUMXth century, the trombone continued to be used mainly in churches. His sound perfectly duplicated the singing voices. The gloomy timbre of the instrument in a low register was excellent for funeral ceremonies.

At the same time, innovative composers drew attention to the sound of the rocker pipe. The great Mozart, Beethoven, Gluck, Wagner used in operas to focus the listener’s attention on dramatic episodes. And Mozart in “Requiem” even entrusted the trombone solo. Wagner used it to convey love lyrics.
At the beginning of the XNUMXth century, jazz performers drew attention to the instrument. In the era of Dixieland, musicians came to the realization that the trombone is capable of creating both solo improvisations and countermelodies. Touring jazz bands brought the scotch trumpet to Latin America, where it became the main jazz soloist.
Types
The trombone family includes several varieties. The tenor instrument is the most commonly used. Design features make it possible to distinguish other representatives of the group:
- alto;
- bass;
- soprano;
- bass.
The last two have almost no use. Mozart was the last to use the soprano rocker trumpet in the Mass in C-dur.

Bass and tenor trombones are in the same tuning. The only difference is in the wider scale of the first one. The difference is 16 inches. The device of the bass colleague is distinguished by the presence of two valves. They allow you to lower the sound by a fourth or raise it by a fifth. Independent structures have more opportunities.
Tenor trombones, in turn, can also have a difference in the diameter of the scale. The smallest diameter of narrow-scaled ones is less than 12,7 millimeters. The difference in size allows the use of different strokes, determines the technical mobility of the instrument.
Tenor scotch trumpets have a brighter sound, a wide range of sound, and are suitable for playing solo parts. They are able to replace al or bass in an orchestra. Therefore, they are the most common in modern musical culture.
Trombone technique
Playing the rocker trumpet is taught in music schools, colleges and conservatories. The musician holds the instrument at his mouth with his left hand, moves the wings with his right. The length of the air column is varied by moving the tube and changing the position of the lips.
The backstage can be located in 7 positions. Each differs from the next one by half a tone. In the first, it is fully retracted; in the seventh, it is fully extended. If the trombone is equipped with an additional crown, then the musician has the opportunity to lower the entire scale by a fourth. In this case, the thumb of the left hand is used, which presses the quarter valve.
In the XNUMXth century, the glissando technique was widely used. The sound is achieved on a continuous extraction of sound, during which the performer smoothly moves the stage.

Outstanding trombonists
Representatives of the Neuschel family belong to the first virtuosos of playing the rocker pipe. The members of the dynasty not only had an excellent command of the instrument, but also opened their own workshop for its manufacture. She was very popular among the royal families of Europe in the XNUMXth-XNUMXth centuries.
The largest number of outstanding trombonists traditionally produce French and German music schools. When graduating from French conservatories, future composers are required to submit several compositions for trombone. An interesting fact was recorded in 2012. Then in Washington, 360 trombonists simultaneously performed on the baseball field.
Among domestic virtuosos and connoisseurs of the instrument, A.N. Morozov. In the 70s he was a leading soloist in the orchestra of the Bolshoi Theater and repeatedly took part in the jury of international trombonist competitions.
For eight years, the best performer in the Soviet Union was V.S. Nazarov. He repeatedly participated in international festivals, became the winner of international competitions, was the leading soloist in the orchestra of Oleg Lundstrem.
Despite the fact that since its inception, the trombone has hardly changed structurally, some improvements have made it possible to expand its capabilities. Today, without this instrument, the full sound of symphonic, pop and jazz orchestras is impossible.





