Piano History
Contents
- History of the piano
- The forerunner of the piano was the monochord
- The mechanism of the piano is the same as that of the dulcimer
- Clavichord – a big step to the piano
- Similarities between piano and harpsichord
- Cristofori, creator of the first piano
- Ancestors of the modern instrument
- Tool values in history
- Piano History in Video
- Conclusion
Piano is a common name for string instruments with hammer action. The ability to play it is a sign of good taste. The image of a diligent, talented musician of the century accompanies every pianist. It can be said that this is an instrument for the elite, although mastering the game on it is an integral part of any musical education.
The study of history helps to better understand the structure and specifics of the works of the past era.
History of the piano
The history of the piano spans more than two centuries. Actually, the first piano was invented simultaneously in America (J. Hawkins at the end of 1800) and Austria (M. Müller at the beginning of 1801). Over time, the developing instrument received pedals. The real form with a cast-iron frame, cross strings, and a multi-level arrangement of dampers developed in the middle of the 19th century.
The most common are “armchair pianos”. They have a standard body size of 1400×1200 mm, a range of 7 octaves, a pedal mechanism mounted on the basement floor, a vertical console connected to the piano leg and beam. Thus, the history of the creation of the piano is almost a hundred years shorter than the era of development of this type of instrument.
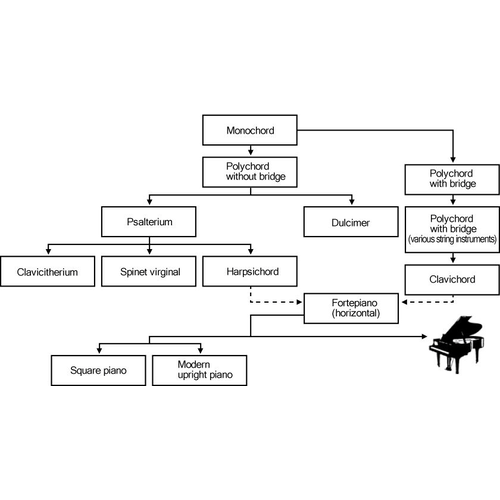
The forerunner of the piano was the monochord
All musical instruments can be divided into three groups depending on the method of sound production. These are string instruments, wind instruments and percussion instruments. Instruments such as the clavichord, harpsichord and dulcimer can be considered the forerunners of the piano. But if we look even further, it becomes clear that the piano is a descendant of the monochord. In other words, based on the history of the origin of the piano, it can be attributed to the group of stringed instruments.
Origin of the piano
The mechanism of the piano is the same as that of the dulcimer

The piano can be classified as a stringed instrument, based on the fact that the sound comes from the vibration of the strings. But it can also be attributed to percussion instruments, because the sound appears due to the blow of the hammers on the strings. This makes the piano related to the dulcimer.
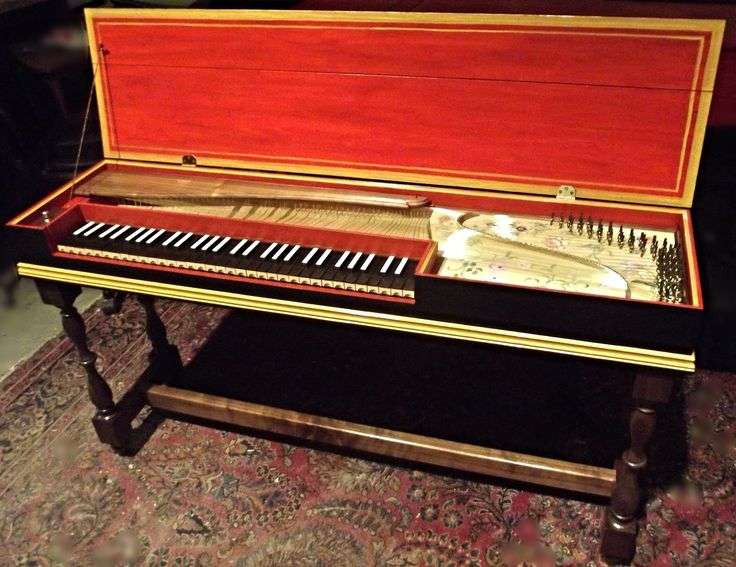
Dulcimer appeared in the Middle East and became widespread in Europe in the 11th century. It is a body with strings stretched from above. As in the piano, a small hammer strikes the strings. This is why the dulcimer is considered the direct predecessor of the piano.
Clavichord – a big step to the piano

The piano also belongs to the family of keyboard instruments. Keyboard instruments have existed since the Middle Ages. They come from an organ on which air is sent through certain tubes to produce sound. The masters improved the organ and developed an instrument that became one step closer to the piano – the clavichord.
The clavichord first appeared in the 14th century and gained popularity during the Renaissance. When a key is pressed, a metal pin with a flat head – a tangent – strikes the string, causing vibration. Thus, it is possible to extract sound in the range from four to five octaves.
Similarities between piano and harpsichord

The harpsichord was created in Italy around 1500 and later spread to France, Germany, Flanders and Great Britain. When a key was pressed, a special rod (spiller) rose to the string, pushing the plectrum, which set the strings in motion.
The system of strings and soundboard, as well as the general structure of this instrument, resembles the structure of a modern piano.
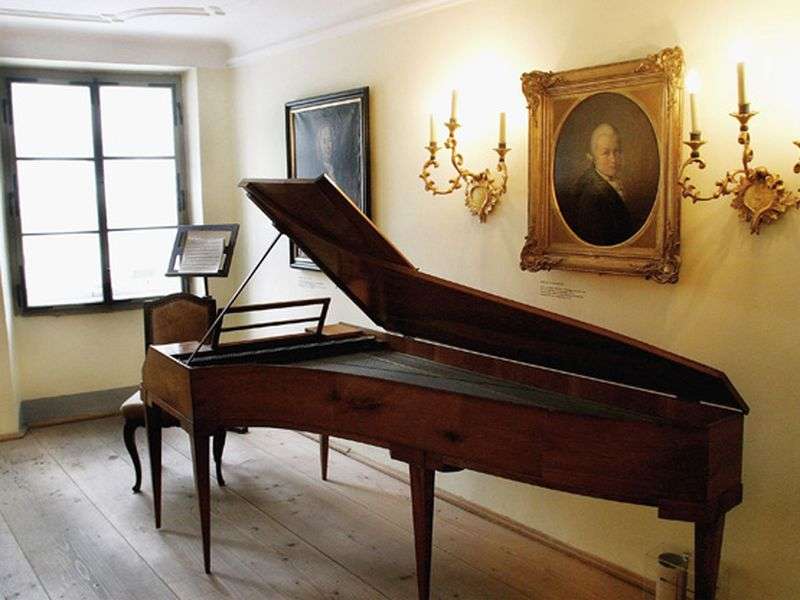
Cristofori, creator of the first piano
The piano was invented by Bartolomeo Cristofori (1655-1731) in Italy.
In the harpsichord, Cristofori did not like the fact that the musicians had little influence on the volume of the sound. In 1709, he replaced the plucked mechanism with a hammer action and created the modern piano.
The instrument was first called “clavicembalo col piano e forte” (harpsichord with soft and loud sound). Later, this name in European languages was shortened to the nowadays accepted “piano”. In Russian, the name closer to the original has been preserved – the pianoforte.

Ancestors of the modern instrument
The most ancient representatives of this class are the clavichord and harpsichord. Who and in what year invented or invented these keyboard-plucked instruments that preceded the piano is not known. Originating around the 14th century, they became widespread in Europe in the 16th-18th centuries.
The difference between the harpsichord is an expressive sound. It is obtained thanks to a rod with a feather attached to the end of the key. This device pulls the string, causing the sound. The peculiarity is low melodiousness, which does not allow to develop dynamic variety, necessitating the device of two keyboards, loud and quiet. Features of the exterior decoration of the harpsichord: elegance and original coloring of the keys. The top keyboard is white, the bottom one is black.
Another forerunner of the piano was the clavichord. Refers to chamber-type instruments. The reeds are replaced by metal plates that do not pull, but touch the strings. This determines the melodious sound, makes it possible to perform a dynamically rich work.
The strength and brightness of the sound is lower, so the instrument was mainly used in home music making, and not at concerts.
The history of the creation of a new instrument and its evolution

Over time, the art of music has become demanding on the quality of dynamics. Old keyboard instruments were gradually modernized. This is how the piano was born. Its inventor is the Florentine Bartalameo Cristofori. Around 1709, the Italian piano maker placed hammers under the strings. This design was called gravicembalo col piano e forte. In France, a similar innovation was developed by J. Marius in 1716, in Germany by K. G. Schroeter in 1717. Thanks to Erar’s invention of the double rehearsal, it was possible to rapidly re-stripe the keys, evoking a more refined and powerful sound. From the end of the 18th century, it confidently replaced the harpsichords and clavichords that had been common before. At the same time, peculiar hybrids arose, combining organ, harpsichord and piano furs.nisms.
The difference between the new instrument is the presence of metal plates instead of reeds. This affected the sound, allowing you to change the volume. The combination of loud (forte) and quiet (piano) sounds on the same keyboard gave the instrument its name. Piano factories gradually sprang up. The most popular enterprises are Streicher and Stein.
In the Russian Empire, Tischner and Wirta were engaged in its development in the 1818-1820s.
Thanks to specialized production, the improvement of the instrument began, which firmly took its place in the musical culture of the nineteenth century. Its design has changed several times. Throughout the century, Italian, German, English craftsmen made improvements to the device. A significant contribution was the work of Silbermann, Zumpe, Schroeter and Stein. Currently, separate traditions of piano production have developed, differing in mechanics . Also, on the basis of the classical instrument, new ones appeared: synthesizers , electronic pianos.
The release of instruments in the USSR, despite the large number, was not of high quality. Factories “Red October”, “Zarya”, ” Accord “, “Lira”, “Kama”, “Rostov-Don”, “Nocturne”, “Swallow” produced inexpensive high-quality products from natural materials, inferior to European counterparts. After the collapse of the Union, the production of pianoforte in Russia practically disappeared.
Tool values in history
The development of the piano was a turning point in musical history. Thanks to his appearance, the concerts in which he took a leading position have changed. This determined the rapid growth in popularity during the period of classicism and romanticism. A galaxy of composers arose who devoted their work exclusively to this instrument. One of the first to master it was W. A. Mozart, J. Haydn, L. Beethoven, R. Schumann, C. Gounod. Numerous masterpieces of piano music are known. Even pieces not intended for the piano sound much more interesting on it than on other instruments.

Piano History in Video
Conclusion
The appearance of the piano is a kind of technical response to the urgent need in musical culture for a new keyboard instrument with a strong sound and a wide range of dynamic shades. Being suitable for playing the best and complex melodies, it has become an invariable attribute of the noble estates and apartments of the modern intelligentsia. And the history of the creation of the piano is a triumphal procession of an ideal instrument.