
How to choose a screen for a projector
Contents
A projection screen is a flat or curved light-scattering surface on which an enlarged image of a film frame, slide, picture, etc. is created using a projector . There are reflective and light-transmitting screens.
Reflective screens have an opaque base, well reflect the light flux falling on them almost evenly in all directions within an angle of 180 °. The image on them is viewed from the side of the projection apparatus. Such screens are installed in all cinemas, except for daytime cinemas, in which films are shown on a light-transmitting screen. The surface of reflective screens, as a rule, is white-matte.
Light-transmitting screens are made of frosted glass, translucent plastic or film-coated fabric. They transmit light rays well, almost without reflecting them. The image on them is viewed from the side opposite to the projection device. Today they are used, in addition to daytime cinema, in advertising and exhibition demonstration installations.

Demonstration on a light-transmitting screen. 19th century
Screen type
For stationary installation, wall-mounted or ceiling-mounted projection screens are used. If you have to move the screen from room to room, and take it with you to outdoor demonstrations, you need to purchase one of the mobile screens.
Screens for stationary installation are rolled or stretched (on a frame). Roll-up screens can be folded and unfolded, tension screens, as the name implies, are stretched on a special frame (included in the kit), and constantly take their place on the wall. This choice, as a rule, is determined by the design and functional features of the room.
 roll screen |  tension screen |
In addition, roll -up projector screens can be either spring-loaded or motorized. Spring-loaded roll screens are unwound by hand and rolled up by means of a spring. Motorized screens are raised and lowered by an electric motor . Motorized screens usually come with wired switches, but a remote control is available as an option.
Mobile screens vary in type of construction and installation. There are desktop screens, as well as several types of floor screen designs. The most popular in terms of price and functionality are tripod screens . They fold easily and quickly and are light in weight. The original screens retractable from the floor housing will interest you primarily for their light weight, ease of installation, as well as excellent design.

Mobile screen on a tripod
Screen surface
Modern screen manufacturers offer various types of surfaces that are aimed at solving one problem: to convey the highest quality image to the viewer. A projection screen can perform one or more of the following tasks: increase the brightness of an image, increase its contrast, and allow light to pass through without reflecting outside light. However, you need to choose the surface very carefully , otherwise part of the audience, and sometimes even all viewers, simply will not see the image.
To begin with, let’s dwell on the main characteristics of surfaces:
1. Gain – a relative value that characterizes the ability of the screen to reflect the light falling on it. The higher it is, the brighter the image will be seen by viewers.
2. Contrast – the ability to accurately reproduce the dark and light areas of the image.
3. The viewing angle characterizes the space in which viewers can comfortably see the image.
A universal solution that will ideally convey the image to any viewer is a matte white surface , designated by manufacturers as Matte White (S, M, P), M1300, Panamax. Such a surface has the largest viewing angle and accurate color reproduction. The gain of this canvas is 1, i.e. It does not increase the brightness of the image, but it does not decrease it either.
To enhance brightness , there are two types of surfaces: reflective (Datalux MFS, Pearlscent) and beaded surface (HighPower, Glass Beaded). The gain of such surfaces varies from 2 to 2.5. The first surface is used when the projector is mounted on the ceiling , because it reflects in the direction opposite to the incidence of rays. The bead cover (glass chip cover) reflects towards the light source and can only be used if the projector is installed at the same level as the audience, for example, on a table in front of the screen. It should also be taken into account that highly reflective surfaces have a limited viewing angle, and viewers sitting away from the center of the screen may not see the picture. These surfaces are used in rooms with bright ambient light, as well as for projectors with low light output.
Gray surfaces (High Contrast, HiDef Grey) are used to enhance contrast . These surfaces have a gain of 0.8-0.9 and a large viewing angle. The ability to render deep blacks without compromising light tones and whites is ideal for rendering any kind of graphic image. This surface is most popular in the creation of home theaters.
Screen Format
This parameter is the ratio of the width of the illustrated image to its height. Many projection devices for home movie viewing come with a 9:16 aspect ratio screen. While for the office version the most suitable screen format is 3:4. To improve the quality of the video image, it is necessary to ensure that the size of the canvas matches the format of the image itself transmitted by the projector.
If you select the wrong screen type, you may see black bars either at the bottom or on the sides of the image.
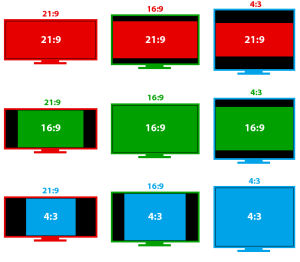
Projection screens appeared long before the advent of video projectors – even at the dawn of the birth of cinema. And this led to such a variety of the ratio of their sides.
- Square format 1:1 . A versatile format that allows you to project both horizontally and vertically oriented images. Photo slides were projected onto such screens, mounted in square frames.
- Photo format 3:2 (1.5:1) . As the name implies, the screen format corresponded to the standard photo frame format.
- Video format 4:3 (1.33:1) . Standard definition TV frame format SD TV.
- Wide 16:9 (1.78:1) . The new high-definition TV format HD TV.
- Widescreen 1.85:1 aspect ratio . A common format for feature films.
- Cinematic aspect ratio 2.35:1 . The widest format in cinema, wider only in panoramic cinemas.
With regard to video projection, it makes sense to talk about only three formats – 1:1, 4:3 and 16:9. If we only need a screen to play regular video , SD or HD , then it remains to choose between 4:3 and 16:9 formats.
The experts of the store “Student” recommend the 4:3 format as the most versatile . On a 4:3 aspect ratio screen, you can always display a 16:9 aspect ratio image by filling the screen width. And if you have a rollable screen, then it can be expanded exactly as much as necessary to play a particular format.
Room settings and screen layout
The screen is optimally selected in such a way that any person present in the room can comfortably parse texts and images on the screen. To calculate the size of the screen canvas, it is recommended to be guided by three basic rules:
- The height of the screen must be at least 1/6 of the distance to the last row of seats in the room
- The distance from the floor to the bottom edge of the screen must be at least 125 cm
- The first row of seats must be at least twice the height of the screen
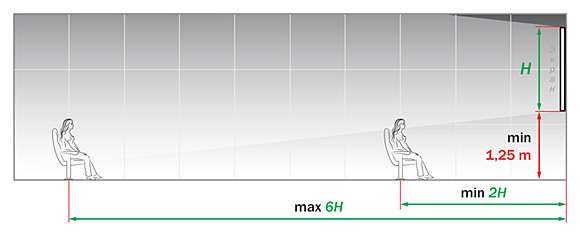
How to choose a projection screen
Projection screen examples
  Projection screen Elite Screens M100XWH-E24 |   Projection screen Elite Screens M150XWH2 |
  Tension screen Elite Screens R135WV1 |   Motorized screen Elite Screens ITE126XW3-E14 |





