
Bagpipe: description of the instrument, composition, how it sounds, history, varieties
Contents
The bagpipe is one of the most original musical instruments invented by man. Traditionally, its name is associated with Scotland, although bagpipe variations are found in almost all European and even some Asian countries.
What is a bagpipe
The bagpipe belongs to the group of reed wind musical instruments. It looks like a bag with tubes protruding randomly from it (usually 2-3 pieces), inside equipped with tongues. In addition to tubes, for a variety of sounds, there may be keys, mortars.

It makes piercing, nasal sounds – they can be heard from afar. Remotely, the voice of the bagpipe resembles guttural human singing. Some consider its sound to be magical, able to have a beneficial effect on well-being.
The range of the bagpipe is limited: only 1-2 octaves are available. It is quite difficult to play, so previously only men were pipers. Recently, women have also been involved in the development of the instrument.
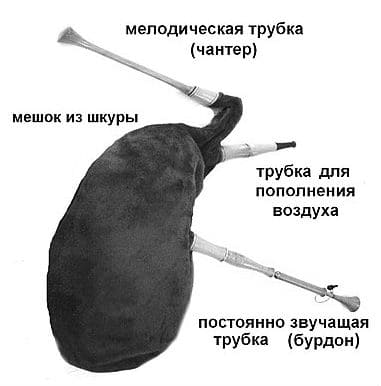
Bagpipe device
The composition of the tool is as follows:
- Storage tank. The material of manufacture is the skin of a pet or its bladder. Usually the former “owners” of the tank, which is also called the bag, are calves, goats, cows, sheep. The main requirement for the bag is tightness, good air filling.
- Injection tube-mouthpiece. It is located in the upper part, attached to the bag with wooden cylinders. Purpose – filling the tank with air. So that it does not come out back, there is a locking valve inside the mouthpiece tube.
- Chanter (melodic pipe). It looks like a flute. Attaches to the bottom of the bag. Equipped with several sound holes, inside there is a reed (tongue), oscillating from the action of air, creating trembling sounds. The piper performs the main melody using a chanter.
- Drones (bourdon pipes). The number of drones is 1-4 pieces. Serve for continuous background sound.
Sound extraction technique
A musician performs music using a melody tube. It has a tip where air is blown in, several side holes. Bourdon tubes, which are responsible for creating background sound, must be adjusted – depending on the piece of music. They emphasize the main theme, the pitch changes due to the pistons in the bourdons.
The story of
It is not known for certain when the bagpipe appeared – scientists are still arguing about its origin. Accordingly, it is not clear where the instrument was invented and which country can be considered the birthplace of the bagpipe.
Similar models of musical instruments have existed since antiquity. The supposed place of origin is called Sumer, China. One thing is clear: the bagpipe arose even before the advent of our era, it was quite popular among ancient peoples, including in Asian countries. Mentions of such a tool, its images are available from the ancient Greeks, Romans.
Traveling around the world, the bagpipe found new fans everywhere. Its traces are found in India, France, Germany, Spain and other states. In Russia, a similar model existed during the period of popularity of buffoons. When they fell out of favor, the bagpipe accompanying the buffoon performances was also destroyed.

The bagpipe is traditionally considered a Scottish instrument. Once in this country, the instrument became its symbol, a national treasure. Scotland is inconceivable without the mournful and harsh sounds made by pipers. Presumably, the tool was brought to the Scots from the Crusades. He enjoyed the greatest popularity among the population living in mountainous areas. Thanks to the inhabitants of the mountains, the bagpipe not only acquired its present appearance, but later became a national instrument.
Bagpipe types
The ancient tool has successfully spread throughout the world, changing along the way, evolving. Almost every nationality can boast of its own bagpipes: having one basis, they at the same time differ from each other. The names of bagpipes in other languages are very diverse.
Armenian
The Armenian folk instrument, arranged like an Irish bagpipe, is called “parkapzuk”. It has a strong, sharp sound. Features: inflating the bag both by the performer and with the help of special bellows, the presence of one or two melodic tubes with holes. The musician holds the bag to the side, between the arm and the body, forcing air inward by pressing the elbow to the body.
Bulgarian
The local name for the instrument is gaida. Has a low sound. Villagers make gaida using the gutted skin of domestic animals (goats, rams). The head of the animal is left as part of the instrument – sound-extracting pipes stick out of it.

Breton
The Bretons were able to invent three varieties at once: the biniu goat (an ancient instrument that sounds original in a duet with a bombarda), the biniu braz (an analogue of the Scottish instrument made by a Breton master at the end of the XNUMXth century), carried (almost the same as the biniu goat, but it sounds great without the accompaniment of the bombarda).
Irish
Appeared at the end of the XVIII century. It was distinguished by the presence of furs that pumped air inside. It has a good range of 2 full octaves.
Kazakh
The national name is zhelbuaz. It is a waterskin with a neck that can be sealed. Worn around the neck, on a lace. Let’s apply in ensembles of folk Kazakh instruments.

Lithuanian-Belarusian
The first written references to the duda, a bagpipe without bourdon, date back to the XNUMXth century. Duda is still actively used today, having found application in folklore. Popular not only in Lithuania, Belarus, but also in Poland. There is a similar Czech instrument worn on the shoulder.
Spanish
The Spanish invention called “gaita” differs from the rest in the presence of a double cane chanter. Inside the chanter there is a conical channel, outside – 7 holes for fingers plus one on the reverse side.

Italian
The most common bagpipes used in the southern regions of the country, called “zamponya”. They are equipped with two melodic pipes, two bourdon pipes.
Mari
The name of the Mari variety is shuvyr. It has a sharp sound, slightly rattling. Equipped with three tubes: two – melodic, one is used to pump air.
Mordovian
The Mordovian design is called “puvama”. It had a ritual meaning – it was believed that it protects from the evil eye, damage. There were two varieties, differing in the number of pipes, the manner of playing.
Ossetian
The national name is lalym-wadyndz. It has 2 tubes: melodic, and also for pumping air into the bag. During the performance, the musician holds the bag in the armpit area, pumping air with his hand.
Portuguese
Similar to the Spanish design and name – gaita. Varieties – gaita de fole, gaita Galician, etc.
Russian
It was a popular instrument. Had 4 pipes. It was superseded by other national instruments.

Ukrainian
It bears the speaking name “goat”. It is identical to the Bulgarian one, when the head is used together with the skin of the animal.
Французская
Different regions of the country have their own varieties: cabrette (single-burdon, elbow type), bodega (single-burdon), musette (court instrument of the XNUMXth-XNUMXth centuries).
Chuvash
Two types – shapar, sarnay. They differ in the number of tubes, musical capabilities.

Scottish
The most recognizable and popular. In folk language, the name sounds like “bagpipe”. It has 5 pipes: 3 bourdon, 1 melodic, 1 for blowing air.
Estonian
The basis is the stomach or bladder of the animal and 4-5 tubes (one each for blowing air and playing music, plus 2-3 bourdon tubes).





