
Drum: description of the instrument, composition, history, types, sound, use
Contents
The drum is one of the most popular and at the same time the most ancient musical instruments. Ease of use, comfortable shape, richness of sounds – all this helps him to remain in demand for the last few thousand years.
What is a drum
The drum belongs to the group of percussion musical instruments. Among the many varieties, the most famous is the membrane drum, which has a dense metal or wooden body, covered with a membrane (leather, plastic) on top.

Sound extraction occurs after hitting the membrane with special sticks. Some musicians prefer punching. For a rich palette of sounds, several models of different sizes, keys are brought together – this is how a drum set is formed.
To date, there are a wide variety of models that differ in shape, size, sound. Known are structures shaped like an hourglass, as well as giant drums, about 2 meters in diameter.
The instrument does not have a certain pitch, its sounds are recorded in a single line, marking the rhythm. Drum roll perfectly emphasizes the rhythm of a piece of music. Small models make dry, distinct sounds, the sound of large drums resembles thunder.
Drum structure
The device of the tool is simple, it consists of the following elements:
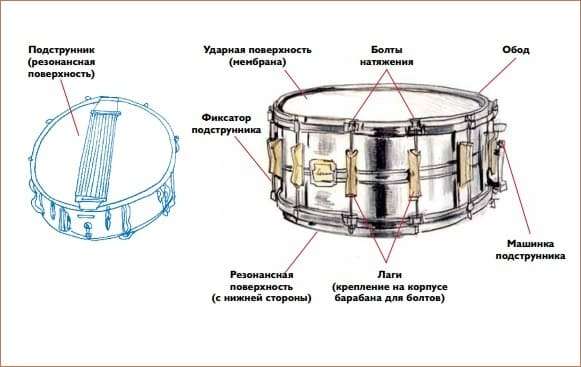
- Frame. Made from metal or wood. The sheet forming the body closes in a circle, being hollow inside. The upper part of the body is equipped with a rim that secures the membrane. On the sides are bolts that serve to tension the membrane.
- Membrane. Stretches on the body both from above and from below. The material for modern membranes is plastic. Previously, leather, animal skins were used as a membrane. The upper membrane is called impact plastic, the lower one is called resonant. The greater the membrane tension, the louder the sound.
- Sticks. They are an integral part of the drum, as they are responsible for sound production. Production material – wood, aluminum, polyurethane. How the instrument will sound depends on the thickness, material, size of the sticks. Some manufacturers label sticks indicating their affiliation: jazz, rock, orchestral music. Professional performers prefer sticks made of wood.
History
By whom and when the ancient drums were invented remains a mystery. The oldest copy dates back to the XNUMXth century BC. An interesting fact is that the tool was distributed all over the world. Each nation had its own drum, slightly different in size or appearance. Among the active admirers of the instrument are the peoples of South America, Africa, and India. In Europe, the fashion for drumming came much later – around the XNUMXth century.
Initially, loud drum sounds were used to signal. Then they began to be used where strict adherence to rhythm was required: on ships with rowers, in ritual dances, ceremonies, and military operations. The Japanese used drum rumble to induce panic in the enemy. The Japanese soldier held the instrument behind his back while he was pounded furiously by two other soldiers.
The Europeans discovered the instrument thanks to the Turks. Initially, it was used in the army: there were specially designed combinations of signals that meant advance, retreat, the beginning of the formation.

Russian soldiers began to use drum-like structures during the reign of Ivan the Terrible. The capture of Kazan was accompanied by the sounds of nakrov – large copper cauldrons covered with leather on top. The ruler Boris Godunov, who preferred foreign mercenaries, adopted from them the custom of fighting with drums that looked like modern models. Under Peter the Great, any military unit included a hundred drummers. At the beginning of the twentieth century, the instrument disappeared from the army. His triumphant return came with the coming to power of the communists: the drum became a symbol of the pioneer movement.
Today, big, snare drums are part of the symphony orchestra. The instrument performs accompanying, solo parts. It is indispensable on the stage: it is actively used by musicians performing in the style of rock, jazz, and the performance of military ensembles is indispensable without it.
A novelty of recent years is electronic models. The musician masterfully combines acoustic and electronic sounds with the help of them.
Types of drums
Types of drums are divided according to the following classifying features:
By country of origin
The instrument is found on all continents, slightly differing in appearance, dimensions, playing methods:
- African. They are a sacred object, take part in religious ceremonies and rituals. Additionally used for signaling. Varieties of African drums – bata, djembe, ashiko, kpanlogo and others.
- Latin American. Atabaque, kuika, conga – brought by black slaves. Teponaztl is a local invention, made from a single piece of wood. Timbales is a Cuban instrument.
- Japanese. The name of the Japanese species is taiko (meaning “big drum”). The “be-daiko” group has a special structure: the membrane is tightly fixed, without the possibility of adjustment. The sime-daiko group of instruments allows you to adjust the membrane.
- Chinese. The bangu is a wooden, one-sided instrument of small size with a cone-shaped body. Paigu is a kind of timpani fixed on a stationary stand.
- Indian. Tabla (steam drums), mridanga (ritual one-sided drum).
- Caucasian. Dhol, nagara (used by Armenians, Azerbaijanis), darbuka (Turkish variety).

By types
Types of drums that form the basis of modern orchestras:
- Big. Bilateral, rarely – one-sided instrument with a low, strong, muffled sound. It is used for single strikes, emphasizing the sound of the main instruments.
- Small. Double-membrane, with strings located along the lower membrane, giving the sound a special touch. The strings can be turned off if the sound is required to be clear, without additional overtones. Used for knocking out shots. You can hit not only the membrane, but also hit the rim.
- Tom-tom. A cylinder-shaped model, descending directly from the indigenous people of America, Asia. In the XNUMXth century, it became part of the drum set.
- Timpani. Copper boilers with a membrane stretched over the top. They have a certain pitch, which the performer can easily change during the Play.

According to the form
According to the shape of the hulls, the drums are:
- Conical,
- Cauldron-shaped,
- “Hourglass”,
- Cylindrical,
- goblet,
- Framework.

Production
Every detail of the drum requires attention, so some craftsmen are engaged in the manual manufacture of the instrument. But professional musicians prefer industrial models.
Materials used to make the case:
- Some types of steel
- bronze,
- Plastic,
- Wood (maple, linden, birch, oak).
The sound of the future model directly depends on the chosen material.
When the case is ready, they begin to manufacture metal fittings: a hoop that secures the membrane, bolts, locks, fasteners. The characteristics of the tool deteriorate significantly if it is equipped with a large number of holes, additional parts. Recognized manufacturers offer a special fastening system that allows you to maintain the integrity of the case.
Drum tuning
Settings require any kind of instrument: having a certain pitch (timpani, rototom) and not having it (tom-tom, small, large).
Tuning occurs by stretching or loosening the membrane. For this, there are special bolts on the body. Too much tension makes the sound too loud, weak tension deprives it of expressiveness. It is important to find the “golden mean”.
A snare drum equipped with strings requires a separate tuning of the bottom membrane.

Using
The instrument is good both in the composition of the ensemble and in the performance of solo parts. The musician independently chooses whether to use sticks when playing or hit the membrane with his hands. Playing with hands is considered the height of professionalism and is not available to every performer.
In orchestras, the drum is given an important role: it is considered the starting point, sets the rhythm of the melody. It goes well with other musical instruments, complements them. Without it, the performances of military bands, rock musicians are inconceivable, this instrument is always present at parades, youth gatherings, and festive events.





