
Basic tone |
Main tone – the dominant sound within a given group of sounds, one of the types of center. element of the corresponding sound system. Distinguish between O. t. interval, chord, tonality (tonic melodic mode), the whole piece, as well as O. t. natural scale. O. t. represents a support, an abutment, a starting point.
O. t. interval – its main sound, subordinating another tone. According to P. Hindemith (1937), the relative position of the difference combination tones indicates the following O. t. in the intervals:
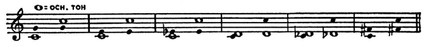
O. t. of a chord is its main sound, according to Krom its essence and meaning in the ladotonality are determined. According to J. F. Rameau (1722), the Ot of a third chord is its “harmonic center” (centre harmonique), which unites the connections between the sounds of the chord. In contrast to the real-sounding basse-continue, Rameau builds another one – basse-fondamentale, which is a sequence of O. t. chords:

Fundamental bass was the first scientific. substantiation of harmonics. tonality. In defining the O. t. of the f-a-c-d type chord in C-dur, Rameau put forward the theory of “double application” (double emploi): if the chord goes further into gghd, its O. t. is the sound d, if in c -g-c-e, then f. The stepped theory of harmony (G. J. Fogler, 1800; G. Weber, 1817; P. I. Tchaikovsky, 1872; N. A. Rimsky-Korsakov, 1884-85; G. Schenker, 1906, etc.) absolutizes the third the principle of constructing chords and takes for O. t. the lower sound of a chord reduced to the main. vidu — a series of thirds; on each sound of the scale as osn. tone, triads and seventh chords (as well as non-chords) are built. In the functional theory of X. Riemann, a distinction is made between O. t. and the prima of a chord (in a major chord, both coincide, in a minor one they do not; for example, in a-c-e O. t. – sound a, but prima – e ). P. Hindemith put forward a new theory of O. T., which is determined by the harmonically strongest and most definite interval for perception (for example, if there is a fifth in a chord, its O. T. becomes O. T. of the entire chord; if fifths no, but there is a quart, the function of the general O. t. is performed by its O. t., etc.). The theory of O. t. Hindemith allows you to analyze the consonances of modern. music, inaccessible to the previous theory and therefore not even considered chords:

Applied in the 20th century. methods of O.’s definition of t. essentially differ from each other. For example, in the chord des-f-as-h (in C-dur, see example): according to the most common step system in school harmony O. t. – the sound h; according to the Hindemith method – des (most obvious to the ear); according to the functional theory of Riemann – g (although it is absent in the chord, it is the main sound of the dominant function.

O. t. tonality (mode) – the main sound, the first step of the modal scale.
In the natural scale – the lower tone, in contrast to the overtones located above it (actually overtones).
References: Tchaikovsky P. I., Guide to the practical study of harmony, M., 1872; Rimsky-Korsakov HA, Harmony Textbook, St. Petersburg, 1884-85; his own, Practical textbook of harmony, St. Petersburg, 1886 (the same, Poln. sobr. soch., vol. IV, M., 1960); Practical course of harmony, parts 1-2, M., 1934-35; Rameau J.-Ph., Traité de l’harmonie reduite a ses principes naturels, P., 1722; Weber G., Versuch einer geordneten Theorie der Tonsetzkunst, Bd 1-3, Mainz, 1817-1821; Riemann H., Vereinfachte Harmonielehre oder die Lehre von den tonalen Funktionen der Akkorde, L. – NY, (1893) his own, Systematische Modulationslehre als Grundlage der musikalischen Formenlehre, Hamb., 1901 (Russian translation. Riemann G., Systematic doctrine of modulation as the basis of the doctrine of musical forms, M. – Leipzig, 1887, 1898); Hindemith R., Unterweisung im Tonsatz, TI. 1929, Mainz, 1.
Yu. H. Kholopov




