
How to choose a classical guitar
Contents
The classical (Spanish, six-string) guitar is a stringed plucked musical instrument. The main representative of the family of guitars in general and acoustic guitars in particular. In its modern form, it has existed since the second half of the 18th century, it is used as a solo, ensemble and accompanying instrument. The guitar has great artistic and performing capabilities and a wide variety of timbres . The main differences from an acoustic guitar are the nylon strings, the wide neck , and the shape of the body.
A classical guitar has six strings, the main structure of which is e1, b, g, d, A, E (mi of the first octave, si, salt, re of a small octave, la, mi of a large octave). A number of musical masters experimented with adding additional strings (ten-string guitar by Ferdinando Carulli and Rene Lakota, fifteen-string guitar by Vasily Lebedev, nine-string, etc.), but such instruments were not widely used.

Vasily Petrovich Lebedev with a fifteen-string guitar
In this article, the experts of the store “Student” will tell you how to choose the classical guitar that you need, and not overpay at the same time. So that you can better express yourself and communicate with music.
guitar construction
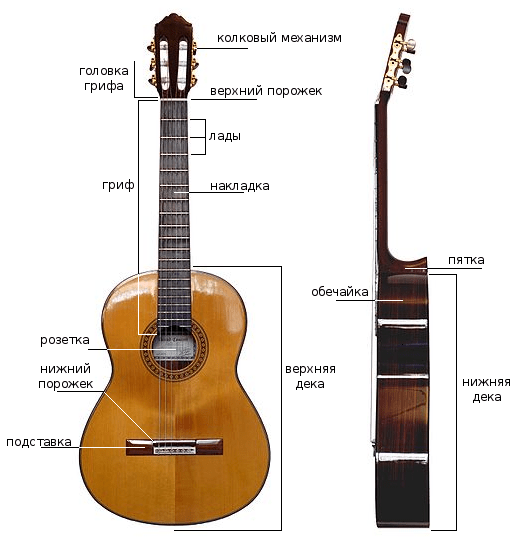
1. Pegs (peg mechanism ) are special devices that regulate the tension of the strings on stringed instruments, and, first of all, are responsible for their tuning like nothing else. Pegs are a must-have device on any stringed instrument.

guitar pegs
2. Nut – a detail of stringed instruments (bowed and some plucked instruments) that raises the string above the fingerboard to the required height.
 Nut _ |  Nut _ |
3. Frets are parts located along the entire length of the guitar neck , which are protruding transverse metal strips that serve to change the sound and change the note. Also fret is the distance between these two parts.
4. Fretboard – an elongated wooden part, to which the strings are pressed during the game to change the note.
5. Neck heel – the place where the neck and the body of the guitar are attached . Usually this concept is relevant for bolted guitars. The heel itself can be bevelled for better access to the frets . Different guitar manufacturers do it in their own way.

Classical guitar neck heel
6. Shell – (from Ch. to twist, wrap something around something) – the side part of the body (bent or composite) of musical instruments. It is easier to say that the shell is the side walls.

shell
7. Upper and lower deck – the flat side of the body of a stringed musical instrument, which serves to amplify the sound.
Guitar size
When properly seated, the guitarist should be able to easily reach the peg responsible for tuning the fourth string. No problem, which means that the arm should not be fully extended, but at least slightly bent at the elbow joint.
The hand rests on the guitar in any part of the forearm (the forearm is part of the arm from the wrist to the elbow), and slightly bent index, middle and ring fingers are able to reach the first, thinnest string. If, reaching for the first string, the hand rests on the guitar at the bend of the elbow, then the guitar is too big.
Dimensions of classical guitars:
4/4 – four-quarter guitar, full standard guitar, suitable for an adult
7/8 – a seven-eighth guitar, slightly smaller than a standard guitar, suitable for those who want a smaller classical guitar
3/4 is a three-quarter guitar, less than a seven-eighth guitar, suitable for 8-11 year old teenagers.
1/2 – guitar one half or half, less than guitar three quarters, suitable for preschool and primary school children 5-9 years old
1/8 – guitar one eighth, suitable for children under the age of 6

Classical guitar dimensions
Types of classical guitars
Veneered ( shell , bottom and deck made of plywood)
Combined ( shell and bottom made of plywood, and deck made of solid cedar or spruce)
From solid wood plates ( shell , bottom and deck completely made of solid wood)
Now let’s look at each of these types in more detail and find out their merits and demerits.
veneered
These guitars are completely made of plywood and only with a small reservation they can be called classical, because such instruments are purely student and fully satisfy this purpose – the first steps in mastering the classical guitar. This type of instrument only looks like a real classical guitar, because it is primarily a market product with a low price / quality ratio. In other words – for little money you get the minimum quality.
Application: elementary classical school, accompaniment, outdoor guitar.
Advantages: low price, durable case.
Disadvantages: poor quality due to savings on materials.

Classical guitar PRADO HS – 3805
Combined
In combined instruments, the bottom and side are made of the same plywood, but the soundboard is made from a single plate of cedar or spruce. This type of classical guitar is already significantly different from conventional veneered guitars. such a deck significantly changes the sound of the six-string and gives it a soft timbre . It is made more carefully and veneered with precious woods.
Very often, many samples of this type of instrument have quite decent and high-quality sound. Classical guitars with a solid wood body are the best choice for many players. for a small amount of money you get an acceptable sound and quite a decent instrument with which you can easily touch the world of classics. The choice of such a guitar is quite justified if your budget is a bit limited. It remains only to choose a good manufacturer.
Application: this guitar is well suited for both studying at a music school and for professional playing. Ideal for accompaniment and considered more of a bardic guitar.
Advantages: for a relatively small amount you get the maximum sound quality. It can also happen that the best example of this type of guitar will be much better than a classical guitar made entirely of solid wood.
Disadvantages: it is probably incorrect to blame these guitars forwhy they weren’t thought of. According to the terms of reference, they are not intended for concert activity, but are only amateur or student. Therefore, their coating and deck thickness are adapted to shocks and careless use, which is not a disadvantage, but rather a specific feature.

Classical guitar YAMAHA CS40
Made from solid wood slabs
Professional classical guitars already belong to this type of instrument , so here the class of the guitar directly depends on the guitar maker, the type of wood (the most valuable is the one that has the highest sound characteristics) and on its procurement process.
When making these guitars, it all starts with choosing the right wood . When the tree is finally selected, its logs are separated, and the blanks are stored for long-term storage for natural drying for several years. During this time, processes occur in the tree that determine its further acoustic properties. After drying, there is a stage of exposure, which directly affects the class of wood, the longer it takes, the more valuable the workpiece is considered.
Application: professional classical guitar, concert activity.
Advantages: the highest quality sound and manufacturing (handmade).
Disadvantages: with the exception of the high cost, there are practically none.
Tips from the store “Student” for choosing a guitar
- The guitar should please you visually . It is also very important what the guitar is made of! If the guitar is made of plywood , then immediately put it aside, no matter how beautiful it is.
- Notice the strings. Classical guitars always have nylon strings. These strings are much easier to learn to play , but they do not have a rich surround sound. The distance between the strings and the neck at the 12th fret must be no more than 3 mm. Check if the outermost strings do not extend beyond the borders of the fretboard plane . In any case, you can always change the strings and choose the most suitable for you personally.
- Inspect the guitar for defects: scratches, cracks, bumps. Often these little things can affect the sound or you may even not be able to set it up properly. Immediately discard the guitar if it has a neck attached to the body with a bolt .
- Ask the seller to tune the guitar and play something. If you hear strings rattling or you just don’t like the sound, then this instrument is not worth buying. Ask the seller for several guitars at once. The more guitars you look at, the more likely you are to choose your instrument.
- Take a close look at the neck of the guitar . It should have an ebony overlay and be perfectly flat . Try to pluck the strings by holding them in different frets . It is very important that they do not rattle. All frets should be even and parallel to each other.
How to choose a classical guitar
Examples of classical guitars
  Classical guitar Cort 100 |   Classical Guitar Yamaha C-40 |
  Classical guitar Strunal 4671-4/4 |   Classical guitar FENDER ESC105 |





